Understanding the human psyche is a superpower in the marketing world. By tapping into psychological frameworks, you can craft strategies that resonate deeply with your target audience, driving engagement and conversions for your products.
This article delves into 10 crucial psychological frameworks in marketing, explaining their essence and demonstrating how you can apply them in real-world marketing scenarios.
Let’s dive in.
1. Social Proof: The Herd Mentality at Work
Social proof underscores the influence of others’ actions and opinions on an individual’s decision-making process. It’s a psychological phenomenon where people assume the actions of others reflect the correct behavior for a given situation.
E-commerce platforms frequently showcase customer testimonials and product reviews. For instance, Amazon highlights user ratings and reviews prominently, encouraging potential buyers by showing that others have had positive experiences with the product.

Social proof extends beyond just showcasing customer reviews. It includes user-generated content, influencer endorsements, media mentions, and social shares. This not only demonstrates popularity but also builds trust through a diversified endorsement strategy.
Spotify, for example, leverages social proof by highlighting playlists that are trending or have been created by celebrities, making users more likely to listen to them based on their popularity and the influence of those they admire.
2. Scarcity: The Fear of Missing Out
Scarcity leverages the human tendency to place higher value on items that are perceived as rare or diminishing in availability.
Limited-time offers on websites like Groupon create a sense of urgency, prompting users to act quickly or risk missing out on a deal.
Scarcity can be about more than just limited-time offers. It can include limited edition products, exclusive memberships, and limited availability notifications. This strategy creates a sense of exclusivity and increases the perceived value of the offer.
Nike releases limited edition sneakers, which not only create urgency but also build a community of collectors and enthusiasts, further amplifying the brand’s appeal through scarcity.
3. Authority: The Expertise Influence
Authority suggests that people are more likely to follow the advice or actions of an expert or authority figure.
Dentist-recommended toothpaste brands use the authority of dental professionals to instill trust and encourage purchases.

Authority is not only about having an expert endorse a product. It’s also about creating authoritative content, earning certifications, and showcasing industry awards. This builds a comprehensive image of expertise and reliability.
WebMD provides health information that is vetted by medical professionals, establishing itself as an authoritative source in the health sector, that users trust for accurate and reliable information.
Quick Read: The AI Marketing Evolution: Opportunities, Challenges!
4. Reciprocity: The Give and Take Principle
Reciprocity involves the human inclination to want to give something back when something is received.
Content marketing strategies, like HubSpot’s offering of free, valuable resources, foster goodwill, making users more inclined to engage with the brand’s services or products.
Google, Microsoft, and other tech giants offer a range of free courses and programs that teach you about Artificial Intelligence and many other valuable skills for the future. So what’s strategy?
Google knows that by providing free training, they get to teach you their methods, tools, and practices to slowly bring you into their cloud and development environment. In addition to that, you will naturally feel a desire to repay the debt for the free training you received. Thanks, Google!
Beyond offering free trials or samples, reciprocity can involve providing exceptional customer service, personalized recommendations, and valuable content without immediate expectation of return. This fosters long-term loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
American Express offers exclusive benefits and personalized services to its card members, creating a sense of being valued that encourages continued loyalty and advocacy for the brand.
5. Loss Aversion: The Fear of Losing Outweighs the Joy of Gaining
Loss aversion highlights that the pain of losing is psychologically twice as powerful as the pleasure of gaining.
Free trial periods for services like Spotify Premium capitalize on loss aversion by offering users all the benefits upfront, making the prospect of losing these benefits after the trial period a powerful motivator to subscribe.
Loss aversion can be heightened by emphasizing what is at stake if an action is not taken, such as missing out on an opportunity to improve one’s life, health, or happiness. This can make the call to action more compelling.
Fitness apps like MyFitnessPal remind users of their daily logging streaks, emphasizing what they stand to lose if they break their streak, thus encouraging continued engagement with the app.
6. Anchoring: The First Impression Sets the Standard
Anchoring occurs when an individual relies too heavily on an initial piece of information to make subsequent decisions.
In pricing strategies, a high initial price set for a product can make all subsequent lower prices seem like bargains, influencing the perceived value and decision-making.
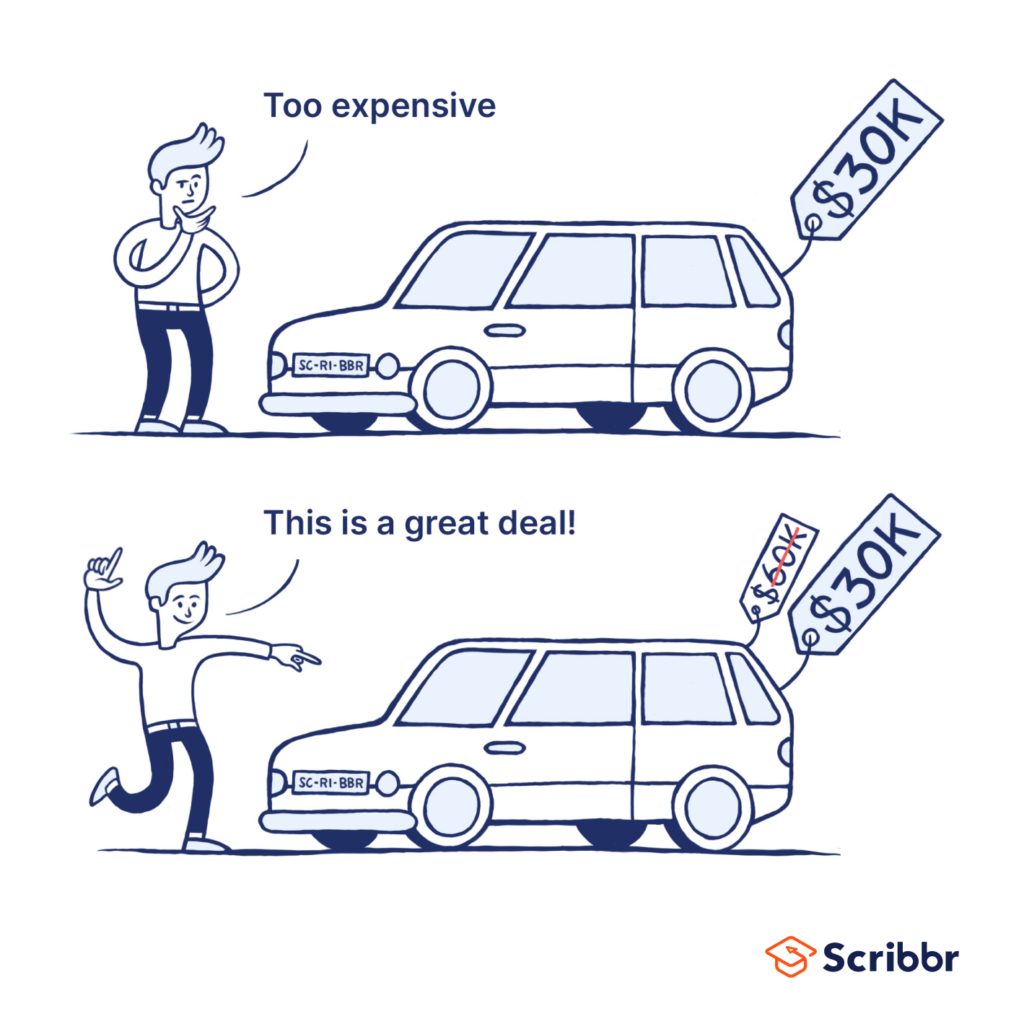
Beyond initial price setting, anchoring can influence how discounts are perceived, how product bundles are valued, and how price comparisons are made. It sets the mental benchmark against which other values are judged.
Tesla showcases its higher-end models alongside their more affordable options, making the latter seem more accessible while maintaining the brand’s premium allure.
7. Framing: Context Matters in Perception
Framing refers to the way information is presented, affecting decision-making and judgment.
A gym membership advertised as “$99 per month” versus “$1,188 per year” uses positive framing to make the cost appear more manageable on a monthly basis. Some may even show weekly pricing or bi-weekly pricing to show the advertised price as low as possible.

Framing goes beyond presenting information positively. It involves crafting the context in which choices are made, such as comparing alternatives in a way that highlights the superiority of one option or framing a decision in terms of gains versus losses.
Insurance companies frame their policies not just as financial protection but as peace of mind and security for one’s family, altering the decision-making context from financial to emotional.
8. Priming: The Subconscious Influence
Priming involves the subconscious influence on people’s perceptions, behaviors, and decisions by means of prior stimuli.
E-commerce sites like Zappos use website design and language that subtly prime visitors with feelings of comfort and ease, making them more likely to make a purchase.
Priming can be achieved through visual cues, language, and even the order in which options are presented. It prepares the consumer’s mind to be more receptive to certain messages or actions.
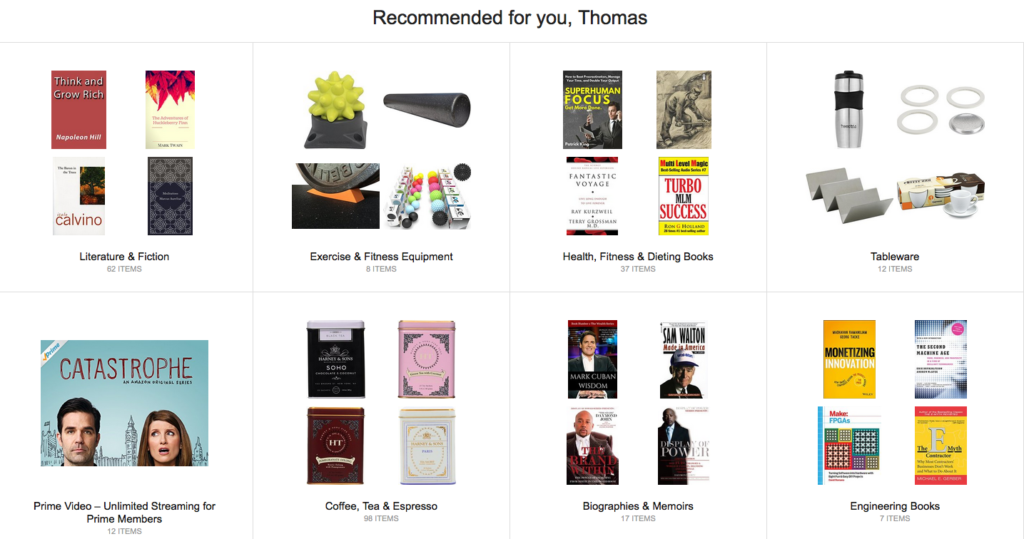
E-commerce websites like Amazon use previous browsing history to prime users with related product recommendations, subtly guiding future purchasing decisions.
9. Bandwagon Effect: The Power of Popularity
The bandwagon effect demonstrates how the popularity of a product or behavior can influence others to adopt it.
Social media platforms display the number of likes, shares, and comments to highlight popularity, encouraging further engagement from users.
Beyond showing popularity metrics, the bandwagon effect can be amplified through community-building, creating viral content, and leveraging social media trends. It creates a sense of belonging and a fear of missing out (FOMO) on a shared cultural experience.
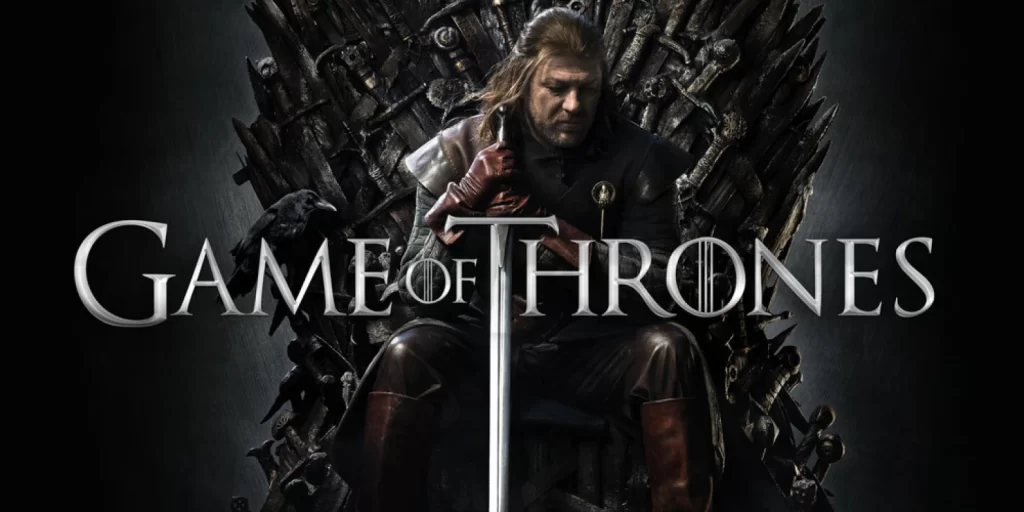

HBO’s Game of Thrones, for example, was released in a way that encouraged binge-watching, prompted social media discussions, and created a sense of urgency to watch to be part of the cultural conversation.
10. Storytelling: Building Connections Through Narrative
Storytelling taps into the human desire for connection and understanding through narrative, making messages more memorable and impactful.
Brands like Apple use storytelling in their marketing to create an emotional connection, showcasing users’ experiences and the impact of their products on everyday life.
Storytelling involves not just narrating a brand’s history or product benefits but weaving a narrative that connects with the audience’s emotions, aspirations, and values. It makes the brand more relatable and memorable.
Airbnb’s “Experiences” not only sell activities but also tell the story of local hosts, their passions, and their unique insights into local culture, making the service more engaging and personal for users.
Your Turn to Try these in the wild!
By integrating these psychological frameworks into marketing strategies, you can more effectively communicate with your audience, driving both engagement and action.
Each framework provides a unique lens through which consumer behavior can be understood and influenced, arming you with a powerful toolkit for crafting compelling marketing messages.






